Running Teleport on GCP
We've created this guide to give customers an overview of how to deploy a self-hosted Teleport cluster on Google Cloud (GCP). This guide provides a high-level introduction to setting up and running Teleport in production.
We have split this guide into:
Teleport Enterprise Cloud takes care of this setup for you so you can provide secure access to your infrastructure right away.
Get started with a free trial of Teleport Enterprise Cloud.
GCP Teleport Introduction
This guide will cover how to set up, configure and run Teleport on GCP.
The following GCP Services are required to run Teleport in high availability mode:
- Compute Engine: VM Instances with Instance Groups
- Compute Engine: Health Checks
- Storage: Cloud Firestore
- Storage: Google Cloud Storage
- Network Services: Load Balancing
- Network Services: Cloud DNS
Other things needed:
Optional:
- Management Tools: Cloud Deployment Manager
- Logging: Stackdriver
We recommend setting up Teleport in high availability mode. In high availability mode Firestore is used for cluster state and audit logs, and Google Cloud Storage is used for session recordings.
Throughout this guide, we'll make use of the following placeholder variables. Please replace them with values appropriate for your environment.
| Name | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|
Example_GCP_PROJECT | teleport-project | Your GCP project ID |
Example_GCP_CREDENTIALS | /var/lib/teleport/google.json | Path to service account credentials |
Example_FIRESTORE_CLUSTER_STATE | teleport-cluster-state | Name of the Firestore collection for Teleport cluster state |
Example_FIRESTORE_AUDIT_LOGS | teleport-audit-logs | Name of the Firestore collection for Teleport audit logs |
Example_BUCKET_NAME | teleport-session-recordings | Name of the GCS bucket for session recording storage |
Compute Engine: VM Instances with Instance Groups
We recommend using n1-standard-2 instances in production. It's best to separate
Teleport's Proxy Servers and Auth Servers using instance groups for each.
Compute Engine: Health Checks
GCP relies heavily on Health Checks, this is helpful when adding new instances to an instance group.
To enable health checks in Teleport start with teleport start --diag-addr=0.0.0.0:3000
see Admin Guide: Troubleshooting for more information.
Storage: Cloud Firestore
The Firestore backend uses real-time updates to keep individual Auth Servers in sync, and requires Firestore configured in native mode.
To configure Teleport to store audit events in Firestore, add the following to
the teleport section of your Auth Server's config file (by default it's /etc/teleport.yaml):
teleport:
storage:
type: firestore
collection_name: Example_FIRESTORE_CLUSTER_STATE
project_id: Example_GCP_PROJECT
credentials_path: Example_GCP_CREDENTIALS
audit_events_uri: [ 'firestore://Example_FIRESTORE_AUDIT_LOGS?projectID=Example_GCP_PROJECT&credentialsPath=Example_GCP_CREDENTIALS' ]
Be careful to ensure that Example_FIRESTORE_CLUSTER_STATE and Example_FIRESTORE_AUDIT_LOGS
refer to different Firestore collections. The schema is different for each, and using the same
collection for both types of data will result in errors.
Storage: Google Cloud Storage
The Google Cloud Storage backend is used for Teleport session recordings. Teleport will try to create the bucket on startup if it doesn't already exist. If you prefer, you can create the bucket ahead of time. In this case, Teleport does not need permissions to create buckets.
When creating the Bucket, we recommend setting it up as Dual-region with
the Standard storage class. Provide access using a Uniform access control
with a Google-managed key.
When setting up audit_sessions_uri use the gs:// prefix.
storage:
...
audit_sessions_uri: 'gs://Example_BUCKET_NAME?projectID=Example_GCP_PROJECT&credentialsPath=Example_GCP_CREDENTIALS'
...
Network Services: Load Balancing
Load Balancing is required for Proxy and SSH traffic. Use TCP Load Balancing as
Teleport requires custom ports for SSH and Web Traffic.
Network Services: Cloud DNS
Cloud DNS is used to set up the public URL of the Teleport Proxy.
Access: Service accounts
The Teleport Auth Server will need to read and write to Firestore and Google Cloud Storage. For this you will need a Service Account with the correct permissions.
If you want Teleport to be able to create its own GCS bucket, you'll need to
create a role allowing the storage.buckets.create permission. You can skip
this step if you choose to create the bucket before installing Teleport.
To create this role, start by defining the role in a YAML file:
# teleport_auth_role.yaml
title: teleport_auth_role
description: 'Teleport permissions for GCP'
stage: ALPHA
includedPermissions:
# Allow Teleport to create the GCS bucket for session
# recordings if it doesn't already exist.
- storage.buckets.create
Create the role using this file:
$ gcloud iam roles create teleport_auth_role \
--project Example_GCP_PROJECT \
--file teleport_auth_role.yaml \
--format yaml
Note the name field in the output which is the fully qualified name for the
custom role and must be used in later steps.
$ export IAM_ROLE=<role name output from above>
If you don't already have a GCP service account for your Teleport Auth Server you can create one with the following command, otherwise use your existing service account.
$ gcloud iam service-accounts create teleport-auth-server \
--description="Service account for Teleport Auth Server" \
--display-name="Teleport Auth Server" \
--format=yaml
Note the email field in the output, this must be used as the identifier for
the service account.
$ export SERVICE_ACCOUNT=<email output from above command>
Lastly, bind the required IAM roles to your newly created service account.
# our custom IAM role allows Teleport to create the GCS
# bucket for session recordings if it doesn't already exist
$ gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding Example_GCP_PROJECT \
--member=serviceAccount:$SERVICE_ACCOUNT \
--role=$IAM_ROLE
# datastore.owner grants the required Firestore access
$ gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding Example_GCP_PROJECT \
--member=serviceAccount:$SERVICE_ACCOUNT \
--role=roles/datastore.owner
# storage.objectAdmin is needed to read/write/delete storage objects
$ gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding Example_GCP_PROJECT \
--member=serviceAccount:$SERVICE_ACCOUNT \
--role=roles/storage.objectAdmin
Download JSON Service Key
The credentials for this service account should be exported in JSON format and provided to Teleport throughout the remainder of this guide.
GCP Quickstart
1. Create Resources
We recommend starting by creating the resources. We highly recommend creating these an infrastructure automation tool such as Cloud Deployment Manager or Terraform.
2. Install & Configure Teleport
Follow install instructions from our installation page.
We recommend configuring Teleport as per the below steps:
- Open Source
- Enterprise
1. Configure Teleport Auth Server using the below example teleport.yaml,and start it
using systemd. The DEB/RPM installations will
automatically include the systemd configuration.
#
# Sample Teleport configuration teleport.yaml file for Auth Server
#
teleport:
nodename: teleport-auth-server
data_dir: /var/lib/teleport
pid_file: /run/teleport.pid
connection_limits:
max_connections: 15000
max_users: 250
log:
output: stderr
severity: DEBUG
storage:
type: firestore
collection_name: Example_FIRESTORE_CLUSTER_STATE
# Credentials: Path to google service account file, used for Firestore and Google Storage.
credentials_path: Example_GCP_CREDENTIALS
project_id: Example_GCP_PROJECT
audit_events_uri: 'firestore://Example_FIRESTORE_AUDIT_LOGS?projectID=Example_GCP_PROJECT&credentialsPath=Example_GCP_CREDENTIALS'
audit_sessions_uri: 'gs://Example_BUCKET_NAME?projectID=Example_GCP_PROJECT&credentialsPath=Example_GCP_CREDENTIALS'
auth_service:
enabled: true
tokens:
- "proxy:abcd123-insecure-do-not-use-this"
- "node:efgh456-insecure-do-not-use-this"
proxy_service:
enabled: false
ssh_service:
enabled: false
1. Configure Teleport Auth Server using the below example teleport.yaml, and start it
using systemd. The DEB/RPM installations will
automatically include the systemd configuration.
#
# Sample Teleport configuration teleport.yaml file for Auth Server
#
teleport:
nodename: teleport-auth-server
data_dir: /var/lib/teleport
pid_file: /run/teleport.pid
connection_limits:
max_connections: 15000
max_users: 250
log:
output: stderr
severity: DEBUG
storage:
type: firestore
collection_name: Example_FIRESTORE_CLUSTER_STATE
# Credentials: Path to google service account file, used for Firestore and Google Storage.
credentials_path: Example_GCP_CREDENTIALS
project_id: Example_GCP_PROJECT
audit_events_uri: 'firestore://Example_FIRESTORE_AUDIT_LOGS?projectID=Example_GCP_PROJECT&credentialsPath=Example_GCP_CREDENTIALS'
audit_sessions_uri: 'gs://Example_BUCKET_NAME?projectID=Example_GCP_PROJECT&credentialsPath=Example_GCP_CREDENTIALS'
auth_service:
enabled: true
license_file: /var/lib/teleport/license.pem
tokens:
- "proxy:abcd123-insecure-do-not-use-this"
- "node:efgh456-insecure-do-not-use-this"
proxy_service:
enabled: false
ssh_service:
enabled: false
The Teleport Auth Service reads a license file to authenticate your Teleport Enterprise account.
To obtain your license file, navigate to your Teleport account dashboard and log in. You can start at teleport.sh and enter your Teleport account name (e.g. my-company). After logging in you will see a "GENERATE LICENSE KEY" button, which will generate a new license file and allow you to download it.
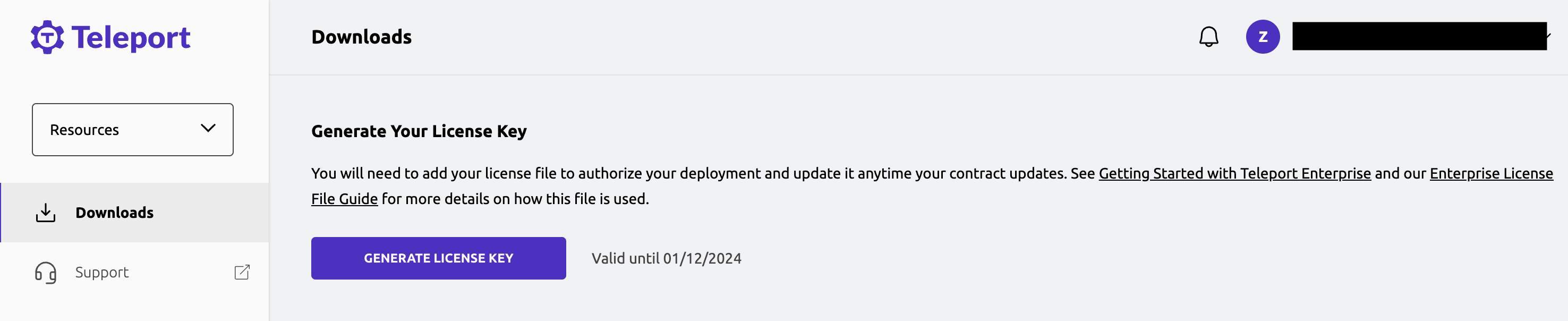
Save your license file on the Auth Servers at the path,
/var/lib/teleport/license.pem.
2. Set up Proxy
Save the following configuration file as /etc/teleport.yaml on the Proxy Server:
# enable multiplexing all traffic on TCP port 443
version: v3
teleport:
auth_token: abcd123-insecure-do-not-use-this
# We recommend using a TCP load balancer pointed to the auth servers when
# setting up in High Availability mode.
auth_server: auth.example.com:3025
# enable proxy service, disable auth and ssh
ssh_service:
enabled: false
auth_service:
enabled: false
proxy_service:
enabled: true
web_listen_addr: 0.0.0.0:443
public_addr: teleport.example.com:443
# automatically get an ACME certificate for teleport.example.com (works for a single proxy)
acme:
enabled: true
email: example@email.com
3. Set up Teleport Nodes
Save the following configuration file as /etc/teleport.yaml on the Node:
version: v3
teleport:
auth_token: efgh456-insecure-do-not-use-this
# Teleport agents can be joined to the cluster via the Proxy Service's
# public address. This will establish a reverse tunnel between the Proxy
# Service and the agent that is used for all traffic.
proxy_server: teleport.example.com:443
# enable the SSH Service and disable the Auth and Proxy Services
ssh_service:
enabled: true
auth_service:
enabled: false
proxy_service:
enabled: false
4. Add Users
Follow our Local Users guide or integrate with Google Workspace to provide SSO access.
