Microsoft SQL Server access with PKINIT authentication
Teleport can provide secure access to Microsoft SQL Server via the Teleport Database Service. This allows for fine-grained access control through Teleport's RBAC.
In this guide, you will:
- Configure your Microsoft SQL Server database with PKINIT authentication.
- Add the database to your Teleport cluster.
- Connect to the database via Teleport.
How it works
The Teleport Database Service joins the same Active Directory domain as the SQL Server database and uses the Kerberos protocol to authenticate with SQL Server. An Active Directory domain is configured to trust the Teleport certificate authority. When a user connects to SQL Server via Teleport, the Database Service uses PKINIT to obtain a ticket-granting ticket from Active Directory. After authenticating, the Teleport Database Service forwards user traffic to the database.
- Self-Hosted
- Teleport Enterprise Cloud
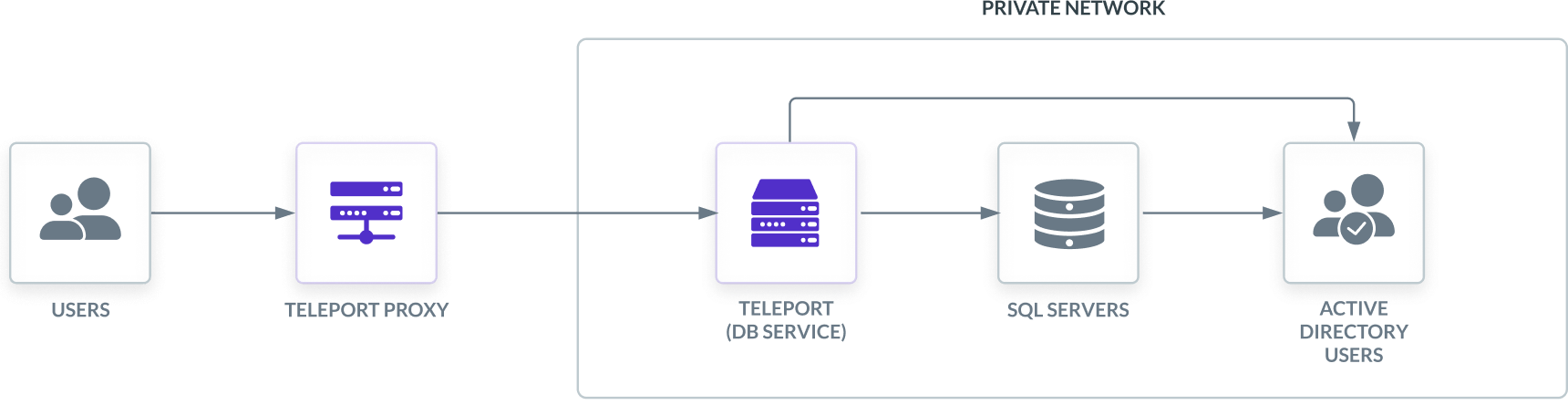
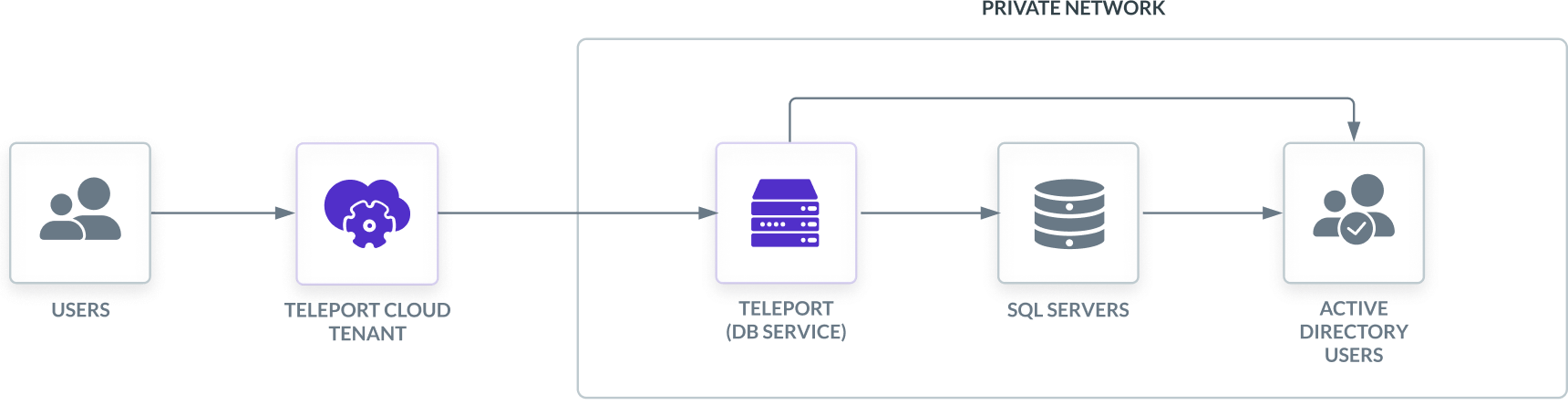
This guide will focus on SQL Servers using self-hosted Active Directory authentication.
Prerequisites
-
A running Teleport cluster version 15.4.22 or above. If you want to get started with Teleport, sign up for a free trial or set up a demo environment.
-
The
tctladmin tool andtshclient tool.On Teleport Enterprise, you must use the Enterprise version of
tctl, which you can download from your Teleport account workspace. Otherwise, visit Installation for instructions on downloadingtctlandtshfor Teleport Community Edition.
-
A SQL Server database with Active Directory authentication enabled.
-
A SQL Server network listener configured with a certificate using Subject Alternative Names.
-
A Windows machine joined to the same Active Directory domain as the database.
-
A Linux node with network access to an Active Directory installation and
kinitcommand with PKINIT extensions installed:- Ubuntu
- RHEL / CentOS 7
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get -y install krb5-user krb5-pkinit$ sudo yum -y update
$ sudo yum -y install krb5-workstation krb5-pkinit -
To check that you can connect to your Teleport cluster, sign in with
tsh login, then verify that you can runtctlcommands using your current credentials.tctlis supported on macOS and Linux machines.For example:
$ tsh login --proxy=teleport.example.com --user=email@example.com
$ tctl status
# Cluster teleport.example.com
# Version 15.4.22
# CA pin sha256:abdc1245efgh5678abdc1245efgh5678abdc1245efgh5678abdc1245efgh5678If you can connect to the cluster and run the
tctl statuscommand, you can use your current credentials to run subsequenttctlcommands from your workstation. If you host your own Teleport cluster, you can also runtctlcommands on the computer that hosts the Teleport Auth Service for full permissions.
Step 1/7. Create a Teleport user
To modify an existing user to provide access to the Database Service, see Database Access Controls
- Teleport Community Edition
- Teleport Enterprise/Enterprise Cloud
Create a local Teleport user with the built-in access role:
$ tctl users add \
--roles=access \
--db-users="*" \
--db-names="*" \
alice
Create a local Teleport user with the built-in access and requester roles:
$ tctl users add \
--roles=access,requester \
--db-users="*" \
--db-names="*" \
alice
| Flag | Description |
|---|---|
--roles | List of roles to assign to the user. The builtin access role allows them to connect to any database server registered with Teleport. |
--db-users | List of database usernames the user will be allowed to use when connecting to the databases. A wildcard allows any user. |
--db-names | List of logical databases (aka schemas) the user will be allowed to connect to within a database server. A wildcard allows any database. |
Database names are only enforced for PostgreSQL, MongoDB, and Cloud Spanner databases.
For more detailed information about database access controls and how to restrict access see RBAC documentation.
Step 2/7. Configure a GPO to allow Teleport connections
We need to configure a GPO to allow Teleport database sessions. This includes telling your computers to trust Teleport's CA and allowing certificate-based smart card authentication.
Export Teleport CA and CRL
You will need to repeat these steps if you rotate Teleport's database certificate authority.
-
Get the Teleport database CA certificate by running:
$ tctl auth export --type=db-client-der > db-ca.cer -
Get the Teleport database CRL by running:
$ tctl auth crl --type=db_client > db-ca.crl -
Transfer the
db-ca.ceranddb-ca.crlfiles to a Windows machine where you can manage your group policy.
Create a GPO and import the Teleport CA
For the purposes of this guide, we apply the GPO we are about to create to our entire AD domain. In the case where you wish for only a subset of computers within your AD domain to be accessible via Teleport, you should apply the GPO to an OU that includes only these computers.
-
Create a GPO named
Teleport DB Access.$GPOName="Teleport DB Access"
New-GPO -Name $GPOName | New-GPLink -Target $((Get-ADDomain).DistinguishedName) -
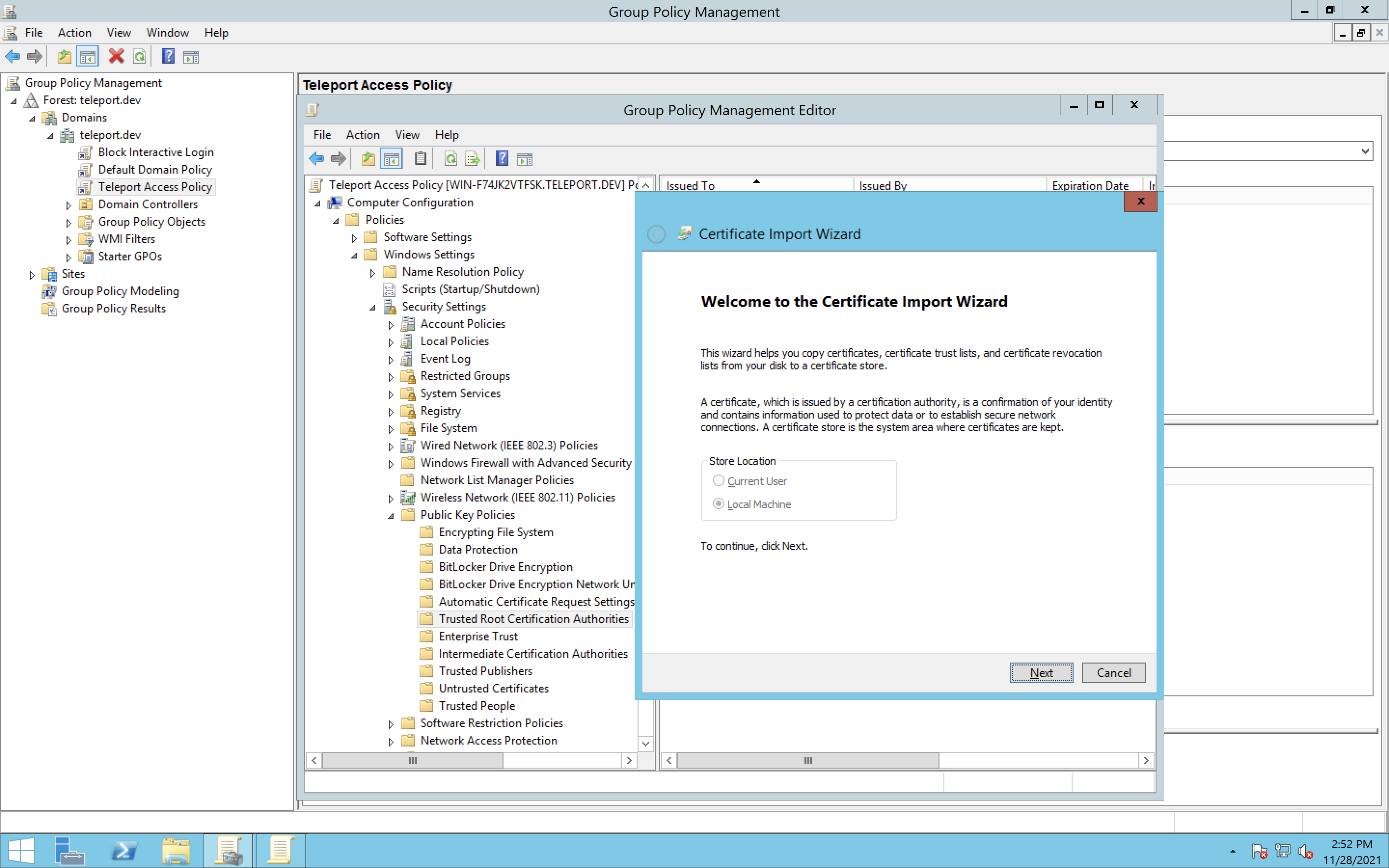
Open the
Group Policy Managementprogram, and on the left pane, navigate to$FOREST > Domains > $DOMAIN > Group Policy Objects. -
Right click on the GPO you just made (
Teleport DB Access), and selectEdit.... -
In the group policy editor, select:
Computer Configuration > Policies > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Public Key Policies -
Right click on
Trusted Root Certification Authoritiesand selectImport. -
Click through the wizard, selecting your CA file (
db-ca.cer).
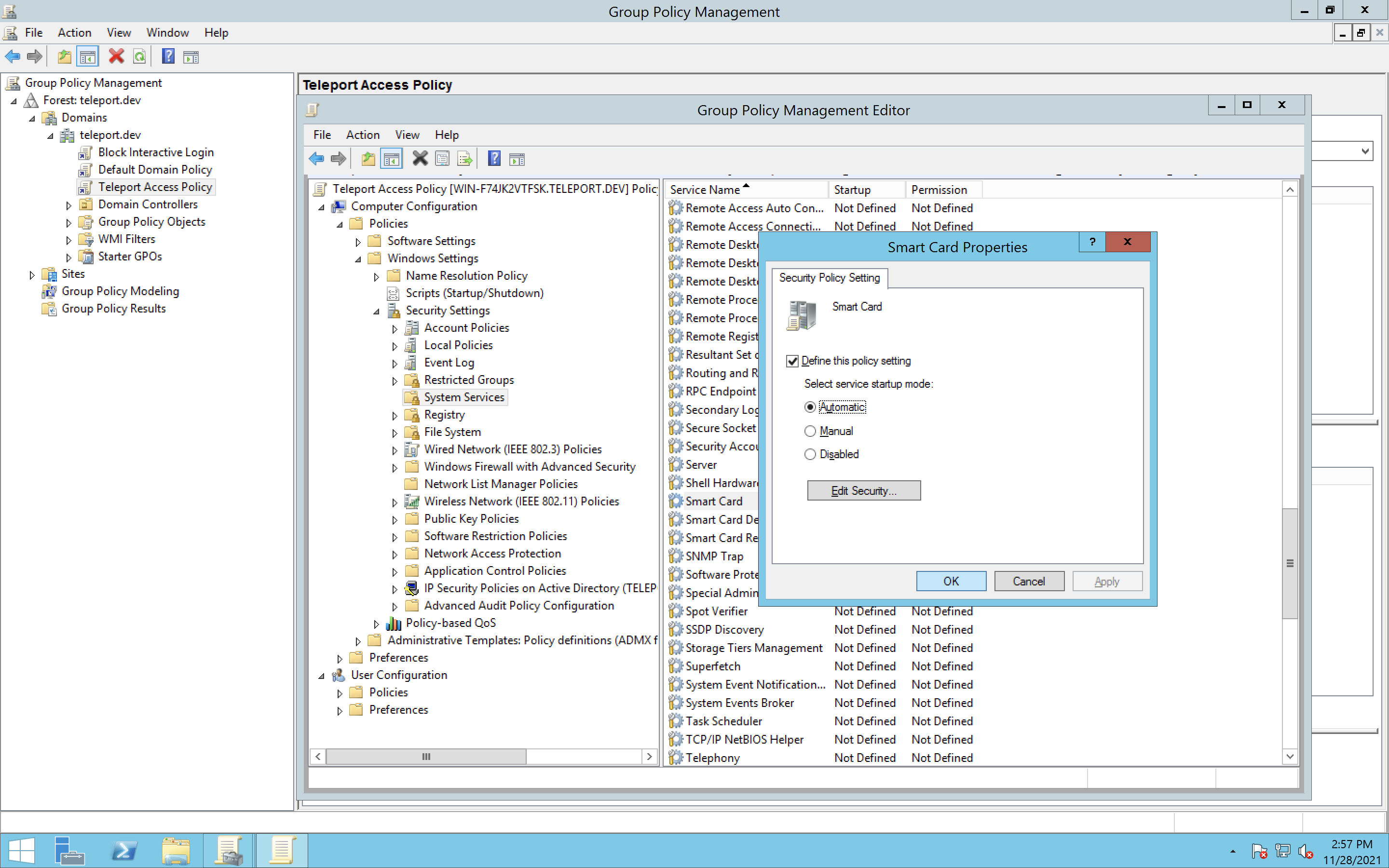
Enable smart card service
Teleport performs certificate-based authentication by emulating a smart card.
-
Still editing your
Teleport DB Access, select:Computer Configuration > Policies > Windows Settings > Security Settings > System Services -
Double click on
Smart Card, selectDefine this policy settingand switch toAutomaticthen clickOK.
You will be modifying GPOs, and sometimes GPO modifications can take some time
to propagate to all hosts. You can force your changes to take effect
immediately on your current host at any time by opening a PowerShell prompt
and running gpupdate.exe /force (though the effects of your changes may still take time to
propagate to other machines on the domain).
Publish the Teleport CA
This step enables the domain controllers to trust the Teleport CA, which will allow smart card logins via Teleport to succeed.
On a machine that is joined to your domain and logged in as an account in the
Domain Administrators group, run the two commands below at a PowerShell prompt
to publish the Teleport CA to your Active Directory domain (using the path
to the exported Teleport db-ca.cer file that you copied above):
certutil –dspublish –f <PathToCertFile.cer> RootCA
certutil -dspublish -f <PathToCertFile.cert> NTAuthCA
Publish the Teleport CRL
On the same machine, run the command below at a PowerShell prompt to publish the
Teleport CRL to your Active Directory domain (using the path to the exported
db-ca.crl file that you copied above).
certutil -dspublish -f <PathToCRLFile.crl> TeleportDB
To avoid waiting until the certificate propagates, you can force the CA retrieval from LDAP after importing the CA and CRL with the command:
certutil -pulse
Step 3/7. Export the LDAP CA certificate
Teleport uses LDAPS to authenticate users, which requires specifying the LDAP CA certificate on the database configuration. To ensure that Teleport trusts the certificate sent by the server during the initial SSL connection, you must export the certificate from your AD. You can export the certificate by running the following PowerShell script on your Windows instance:
$WindowsDERFile = $env:TEMP + "\windows.der"
$WindowsPEMFile = $env:TEMP + "\windows.pem"
certutil "-ca.cert" $WindowsDERFile
certutil -encode $WindowsDERFile $WindowsPEMFile
$CA_CERT_PEM = Get-Content -Path $WindowsPEMFile
Write-Output $CA_CERT_PEM
Remove-Item $WindowsDERFile -Recurse
Remove-Item $WindowsPEMFile -Recurse
The script will write the LDAP CA contents in PEM format to the terminal, and from there, you can copy and use it on your database configuration.
Step 4/7. Set up the Teleport Database Service
The Database Service requires a valid join token to join your Teleport cluster.
Run the following tctl command and save the token output in /tmp/token
on the server that will run the Database Service:
$ tctl tokens add --type=db --format=text
abcd123-insecure-do-not-use-this
Install Teleport on the host where you will run the Teleport Database Service:
Install Teleport on your Linux server:
-
Assign edition to one of the following, depending on your Teleport edition:
Edition Value Teleport Enterprise Cloud cloudTeleport Enterprise (Self-Hosted) enterpriseTeleport Community Edition oss -
Get the version of Teleport to install. If you have automatic agent updates enabled in your cluster, query the latest Teleport version that is compatible with the updater:
$ TELEPORT_DOMAIN=example.teleport.com
$ TELEPORT_VERSION="$(curl https://$TELEPORT_DOMAIN/v1/webapi/automaticupgrades/channel/default/version | sed 's/v//')"Otherwise, get the version of your Teleport cluster:
$ TELEPORT_DOMAIN=example.teleport.com
$ TELEPORT_VERSION="$(curl https://$TELEPORT_DOMAIN/v1/webapi/ping | jq -r '.server_version')" -
Install Teleport on your Linux server:
$ curl https://cdn.teleport.dev/install-v15.4.22.sh | bash -s ${TELEPORT_VERSION} editionThe installation script detects the package manager on your Linux server and uses it to install Teleport binaries. To customize your installation, learn about the Teleport package repositories in the installation guide.
Copy the join token to a file on the instance where you will run the Database Service, and then use the following configuration, replacing the fields on the database section below as appropriate:
uri: The server address, including the port.domain: The Active Directory domain (Kerberos realm) DNS/Address to which SQL Server is joined.spn: Service Principal Name (SPN) for SQL Server to fetch Kerberos tickets.kdc_host_name: SPN of the domain controller responsible for providing the LDAP CA.ldap_cert: The contents of the LDAP CA previously exported.
version: v3
teleport:
auth_token: abcd123-insecure-do-not-use-this
proxy_server: teleport.example.com:443
auth_service:
enabled: no
ssh_service:
enabled: no
proxy_service:
enabled: no
db_service:
enabled: "yes"
databases:
- name: my-sqlserver
protocol: sqlserver
uri: SQL-SERVER-INSTANCE.ad.teleport.dev:1433
ad:
domain: ad.teleport.dev
spn: MSSQLSvc/SQL-SERVER-INSTANCE.ad.teleport.dev:1433
kdc_host_name: DOMAIN-CONTROLLER.ad.teleport.dev
ldap_cert: |
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
...
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
You can look SPNs up in the Attribute Editor of the Active Directory Users and Computers dialog on your AD-joined Windows machine.
If you don't see the Attribute Editor tab, make sure that the "View > Advanced Features" toggle is enabled.
Step 5/7. Start the Database Service
Start the Teleport Database Service in your environment:
Configure the Database Service to start automatically when the host boots up by creating a systemd service for it. The instructions depend on how you installed the Database Service.
- Package Manager
- TAR Archive
On the host where you will run the Database Service, enable and start Teleport:
$ sudo systemctl enable teleport
$ sudo systemctl start teleport
On the host where you will run the Database Service, create a systemd service configuration for Teleport, enable the Teleport service, and start Teleport:
$ sudo teleport install systemd -o /etc/systemd/system/teleport.service
$ sudo systemctl enable teleport
$ sudo systemctl start teleport
You can check the status of the Database Service with systemctl status teleport
and view its logs with journalctl -fu teleport.
Step 6/7. Create SQL Server AD users
You can skip this step if you already have Active Directory logins in your SQL Server.
Connect to your SQL Server as an administrative account (e.g. sa) and create
logins that will use Active Directory authentication:
master> CREATE LOGIN [EXAMPLE\alice] FROM WINDOWS WITH DEFAULT_DATABASE = [master], DEFAULT_LANGUAGE = [us_english];
Step 7/7. Connect
Log in to your Teleport cluster. Your SQL Server database should appear in the list of available databases:
- Self-Hosted
- Teleport Enterprise Cloud
$ tsh login --proxy=teleport.example.com --user=alice
$ tsh db ls
# Name Description Labels
# --------- ------------------- -------
# sqlserver env=dev
$ tsh login --proxy=mytenant.teleport.sh --user=alice
$ tsh db ls
# Name Description Labels
# --------- ------------------- -------
# sqlserver env=dev
To retrieve credentials for a database and connect to it:
$ tsh db connect --db-user=teleport sqlserver
Either the sqlcmd or mssql-cli command-line clients should be available in
PATH in order to be able to connect. tsh attempts to run sqlcmd first and,
if it's not present on the PATH, runs mssql-cli.
If you have neither command-line clients available on your system, you can run the following command to start a local proxy server that you can connect to with your SQL Server client:
$ tsh proxy db --db-user=teleport --tunnel sqlserver
Read the Database Access GUI Clients guide for how to connect your DB GUI client to the local proxy.
To log out of the database and remove credentials:
$ tsh db logout sqlserver
Troubleshooting
Teleport CA and CRL not imported correctly
When connecting to your database, you get an error Error message: authentication failed and Teleport Database Service logs have the error message Failed to authenticate with KDC: kinit: Client not trusted while getting initial credentials. This happens when the Teleport Database CA is not imported
correctly or propagated yet. You can force the propagation by running
certutil -pulse and trying to connect to your database.
Invalid KDC hostname
If you’re connecting to your database and receive the error Error message: authentication failed and on Teleport Database Service logs, there is the error
entry Failed to authenticate with KDC: Password for user@AD.TELEPORT.DEV: \nkinit: Cannot read password while getting initial credentials, which means
that the KDC hostname is wrong. You can verify your domain controller’s SPN to
see if they’re set correctly and update the value on the field kdc_hostname on
your database's configuration.
Teleport cannot verify database CA
If your database has a CA that Teleport doesn’t know about, it will return the
following error when connecting to it: Error message: TLS Handshake failed: x509: certificate signed by unknown authority (possibly because of "x509: invalid signature: parent certificate cannot sign this kind of certificate" while trying to verify candidate authority certificate "SSL_Self_Signed_Fallback").
To solve this, you can add the following configuration to your Teleport Database Service instance:
...
db_service:
databases:
- name: sqlserver
protocol: sqlserver
+ tls:
+ # Point it to your Database CA PEM certificate.
+ ca_cert_file: "rdsca.pem"
+ # If your database certificate has an empty CN filed, you must change
+ # the TLS mode to only verify the CA.
+ mode: verify-ca
ad:
...
If you’re unable to acquire the database CA, you can skip TLS verification by
providing the configuration tls.mode: "insecure". However, we do not recommend
skipping TLS verification in production environments.
Next steps
- Learn how to restrict access to certain users and databases.
- View the High Availability (HA) guide.
- Take a look at the YAML configuration reference.
- See the full CLI reference.